by The Curious Scribbler
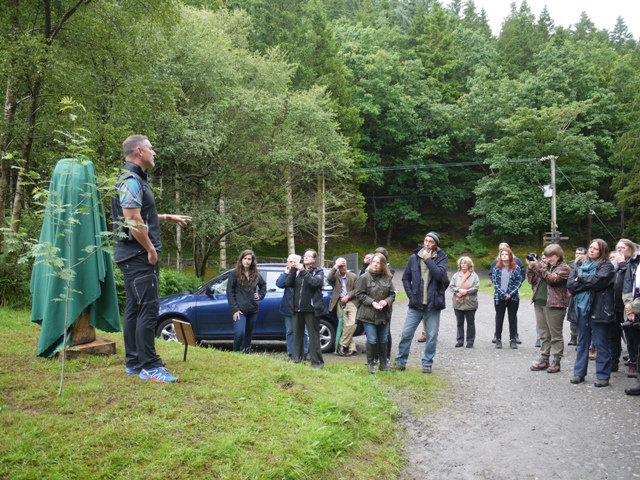

Iolo Williams addresses the Vincent Wildlife Trust’s guests in the Hafod car park
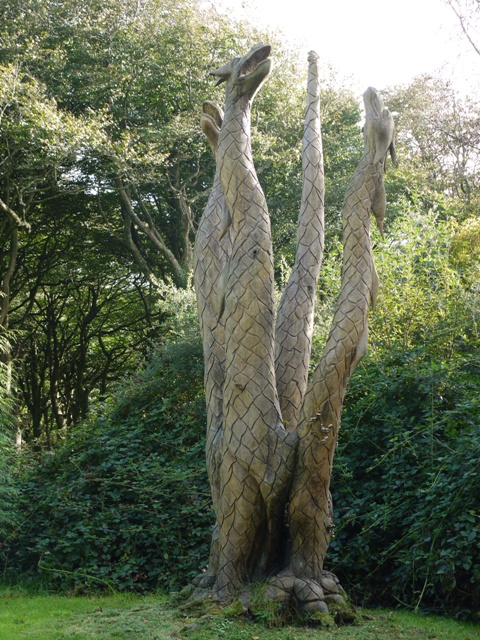
About eighty people gathered yesterday in the car park beside Hafod Church to witness the unveiling, by Wales’ premier TV naturalist Iolo Williams, of a curious sculpture. Its designation plaque, as a memorial to Rob Strachan ‘an inspirational naturalist and conservationist’ might make one wonder whether it would not be more appropriately placed inside the churchyard wall. However it has perhaps a wider purpose, for it was installed by the Vincent Wildlife Trust whose project is the reintroduction of pine martens into NRW ( National Resources Wales, fomerly the Forestry Commission) woodlands in Wales. A pine marten and two kits are represented on the sculpture by Grace Young Monaghan. It is carved from an oak trunk sourced from the estate, though puzzlingly the trunk has been adzed to resemble no British tree. Call me a pedant, but I find this jarring. Four oak leaves are represented, like a label on the trunk, but why is its bark represented with horizontal rather than vertical fissures? Has it been attacked by a giant beaver?
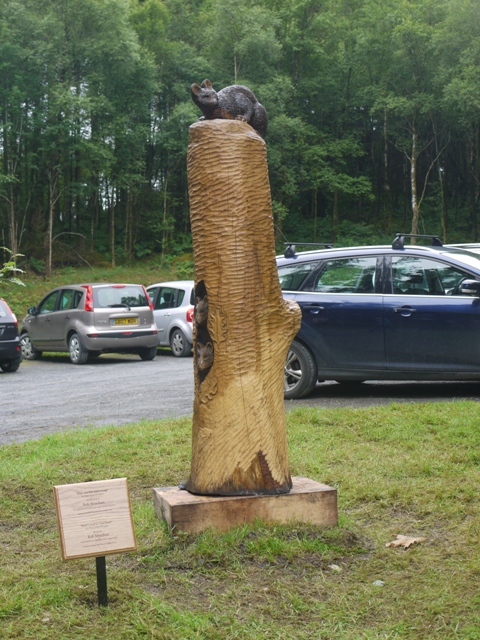

Pine marten sculpture in Hafod car park
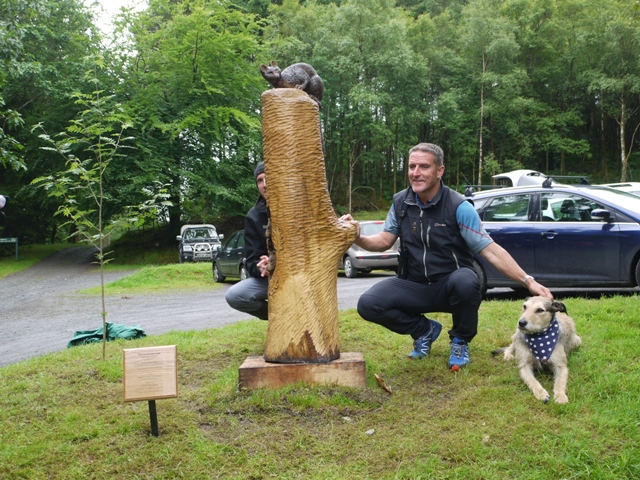

Project Officer Dave Bavin , his dog, and Iolo Williams pose beside the sculpture
The effigy may serve though to alert visitors to the estate to the slim possibility of glimpsing one of these elegant mustelids in the woods. In the last two Septembers 39 Scottish pine martens have been trapped, driven by air-conditioned van from Scotland, and penned and then released at Hafod. Although most of the first batch of introductions in 2015 dispersed or died, one female from this group has produced kits at Hafod, conceived and born this year, and several of last September’s shipment, who will have arrived pregnant, have successfully produced young this spring. Most have spurned the man-made box dens provided for them near the release sites, and have instead sought out dens of their own choosing.
Martens are solitary and occupy large territories, so I wondered how the researchers on the project keep tabs upon the animals. I learned that the privacy of these pioneer pine martens is considerably compromised. First of all, each immigrant is DNA profiled by a lab in Ireland before release. Fitted out wearing radio collars their presence can be monitored by a volunteer sitting in their car on the forest drives or strolling the woods with a receiver like a TV aerial. Thus the approximate location can be determined without need of a visual sighting. Some of the first batch of Hafod-released animals were disinclined to remain and were found far, far away. One female eventually settled near Abergele! Recently, the Vincent Wildlife Trust has also had success with GPS transmitters which can provide researchers with accurate location from much further away.
The martens are also monitored by motion sensitive cameras in the woods. Now it might seem one would have to wait a long time to see a marten stroll by, but the odds are considerably enhanced by putting out bait. Martens proved particularly partial to jam sandwiches and peanut butter, and will return regularly to a bait site in front of the camera in order to check whether it has been replenished. One mother’s successful breeding was revealed when she led her kits into camera range to join the feast. The same inducements work well to lure the martens into traps so that their health can be monitored, or, before the battery runs out, their collars can be removed or replaced.
DNA technology given further insights. A fresh scat ( droppings) can reveal the DNA profile of the perpetrator. Since all the introduced martens have been profiled, a poo sample can even reveal the parentage of a new kit. For long, the analysis of droppings has been a valuable tool in discovering the dietary preferences of mammals. To this, modern mammologists can now add the identity and geneaology of the marten who dealt it!
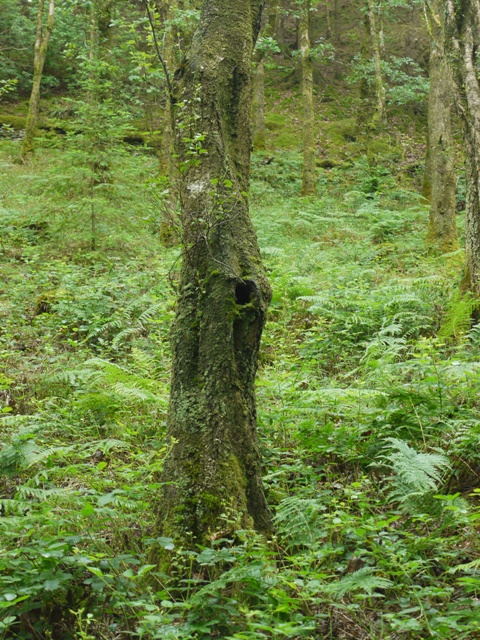

Just the sort of tree hole to appeal to a pine marten
I was impressed by the youth and enthusiasm of the Vincent Wildlife Trust researchers and volunteers who gathered for this celebration. But even for them, equipped with 21st century tracking technology, the best sightings of these elusive animals are probably those from the daylight and night-vision remote cameras. Some of the highlights of camera trap photography can be found among Vincent Wildlife Trust uploads on vimeo. Scat is a little easier to find, because martens typically deposit it in prominent positions, on paths or on an eminence like a tree stump.