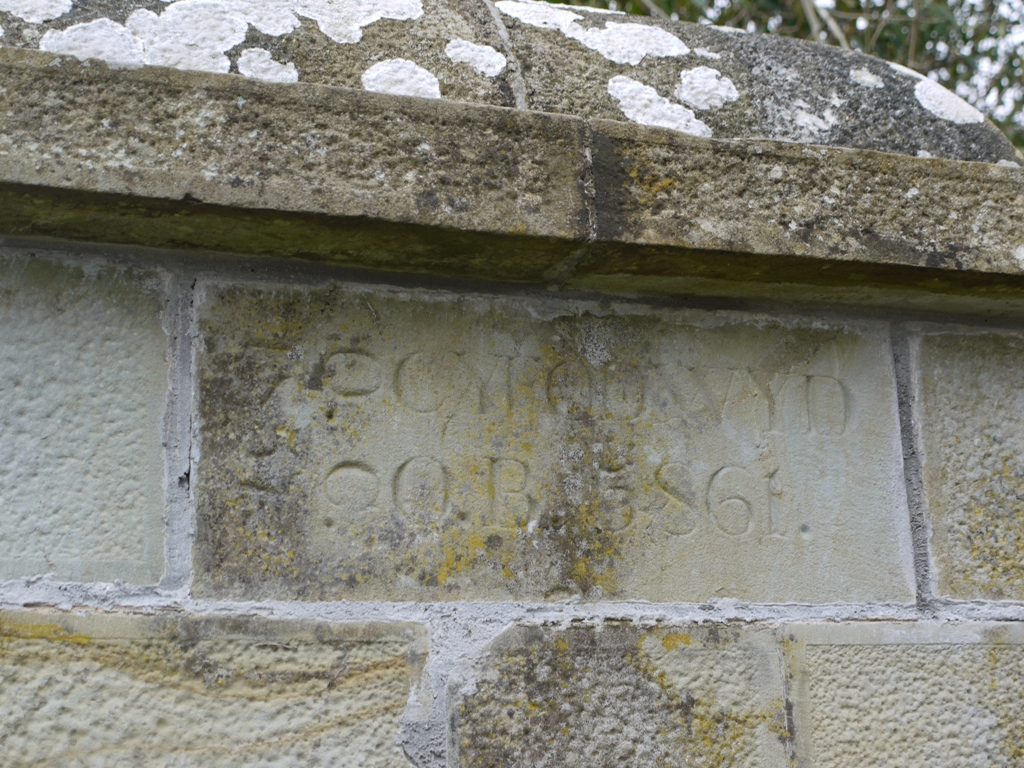We found some puzzling inscriptions on last week’s visit to South Ceredigion.
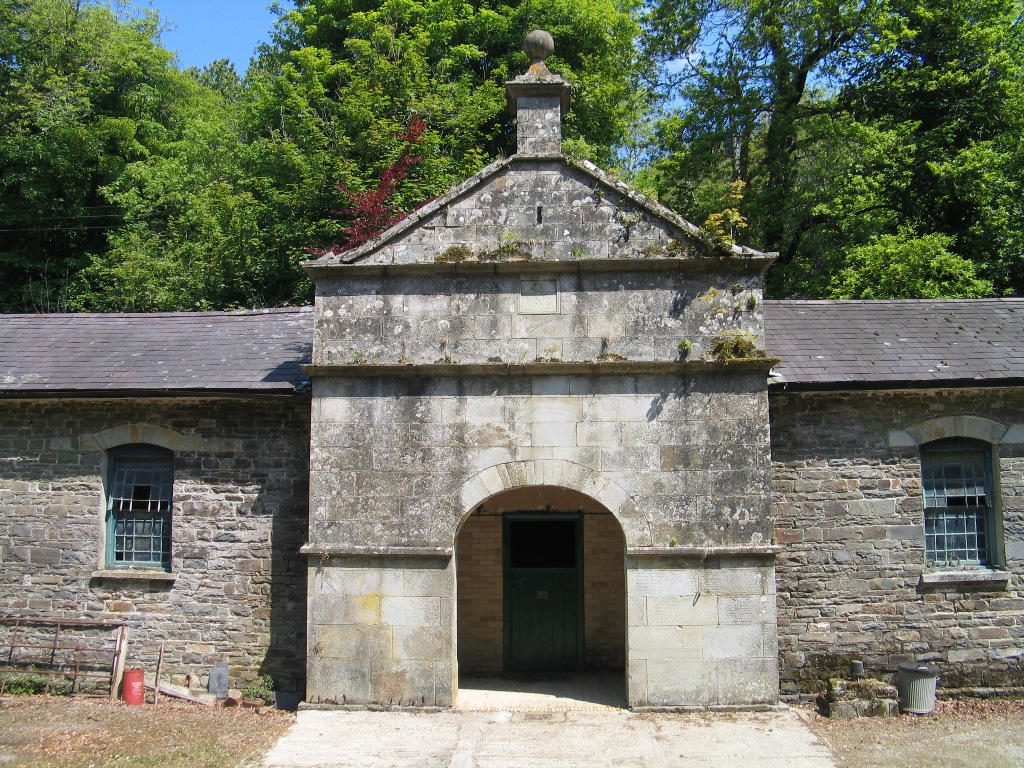
At Alltyrodin we went to view the handsome stable block adjoining the Georgian house. The central doorway is set in large ashlar blocks from the nearby estate quarry, Gwarallt at Bwlchyfadfa.
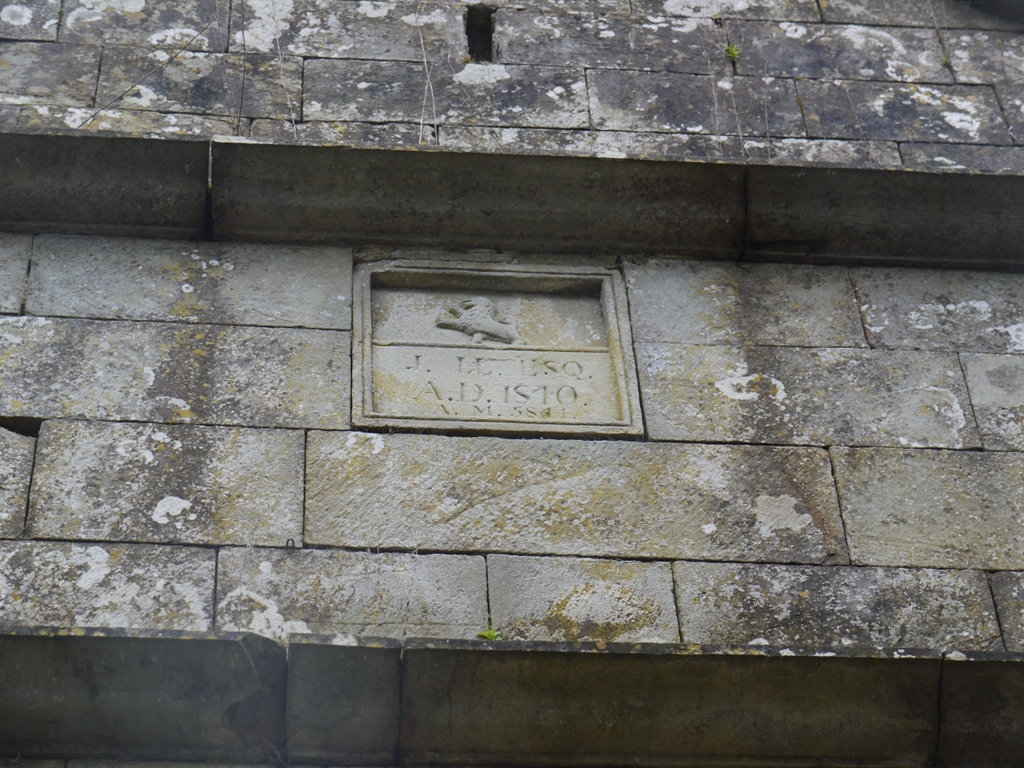
And above the door is a carved plaque with lion rampant which reads:
J LL Esq.,
AD 1840
AM 5841
J LL represents John Lloyd, who inherited Alltyrodin on the death of his older brother David in 1822. He was unmarried and childless ( though there is a deed for a prenuptial settlement in 1826, when he was about to marry Dorothy Alicia Seymer of Bath, spinster) He was still alive and signing deeds in 1836. On his death his estate duly passed to his niece and her husband John Lloyd Davies is identified as master of Alltyrodin by 1843.
AM 5841 represents the date as Anno Mundi; years since the alleged creation of the earth. It is a slightly problematical date. Bishop Ussher (1581 – 1656) decided upon 21 September 4004BC for the creation of the earth, while the Masonic convention is to use 4000 years. Jewish sources use 3761 years BC instead. Assuming the stables were completed in or after September 1840, the carving is consistent with the Masonic convention: 4000 plus 1840 plus 1 if after September, would generate the observed date Anno Mundi 5841. Fairly easy to interpret, then, except that the modern Masonic Dictionary would designate a date of AD plus 4000 years as Anno Lucis, and AD plus 3761 as Anno Mundi. Perhaps they thought differently in the 19th century.
Not far away at Bwlchbychan a handsome gateway with three posts and connecting walls frames the drive down to the house. Here the mason is identified in the inscription as D James mason. The sandstone blocks are neatly stippled with chisel marks like those remarked on at the chapel inTanygroes in the foregoing blog.
On one post the inscribed plaque reads Erected 5861 and the other bears the same information Cyfodwyd (was raised) in Welsh and the year 5861. Assuming the same convention, these gateposts went up in autumn 1860, and this looks consistent with their architectural style. At Bwlchbychan the dating is uncorroborated Anno mundi, whereas at Alltyrodin the more familiar Anno domini date appears larger, and above.
The house was home in the 19th century to John Pugh Vaughan Pryse, third son of Pryse Pryse of Gogerddan. Shortly after his second marriage (to Decima Dorothea Rice of Lwynybrain), it was rebuilt in 1850 “ in the plain domestic style of architecture”, and presumably the gateposts and lodge were built shortly after. Herbert Vaughan in his book, The South Wales Squires, described it as a rather dismal house and its occupant John Pugh Vaughan Pryse as a man who chased the fox as often as he could: ” in the dining room alone were 30 foxes masks, varied by a few heads of hares and otter’s poles. On the hearth rug lay a footstool comprised of a complete stuffed fox.” Pryse died in 1903, at the age of 85.
It is not clear to me whether these Anno Mundi dates indicate membership of the Freemasons on the part of the squires of Alltyrodin and Bwlchbychan, or whether instead they represent the beliefs of the actual masons who worked the stone on their behalf.